Understanding Custom Injection Molding: Materials
The selection of materials used in Custom Injection Molding depends on various factors such as desired properties, application requirements, and cost-effectiveness.
One commonly used material in custom injection molding is thermoplastics. These versatile polymers can be melted and solidified multiple times without losing their properties. Thermoplastics offer a wide range of options in terms of strength, flexibility, and durability, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
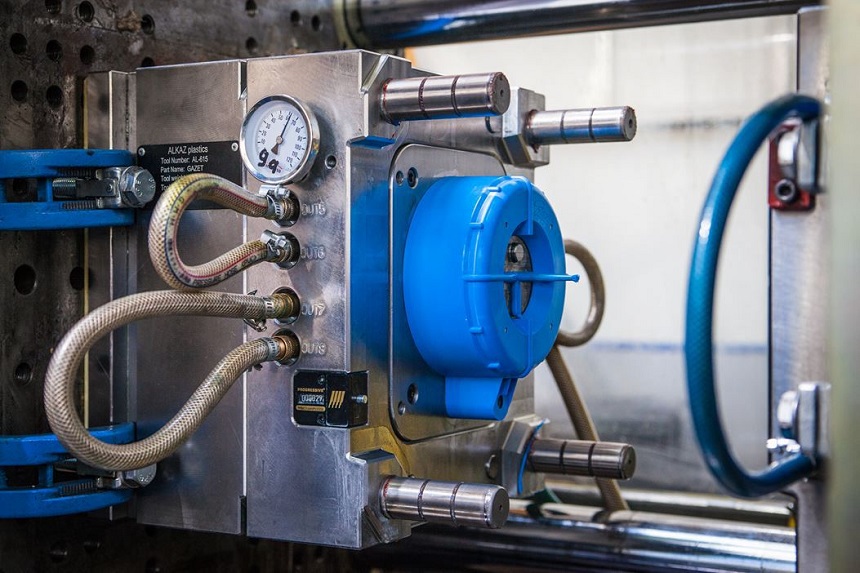

Another popular choice is thermosetting plastics. Unlike thermoplastics, once these materials are molded and cured through heat or chemical reactions, they cannot be re-melted or re-shaped. This makes them ideal for applications that require high temperature resistance or superior dimensional stability.
Metal alloys are also utilized in custom injection molding for specific applications that demand exceptional strength and durability. These alloys provide excellent mechanical properties while retaining their shape under extreme conditions.
Furthermore, elastomers or rubber-like materials are used when flexibility and elasticity are key requirements for the end product. Elastomers offer excellent resistance to abrasion, impact, and harsh environmental conditions.
In addition to these primary materials, additives such as fillers (e.g., glass fibers), colorants, stabilizers, and flame retardants can be incorporated into the custom injection molding process to enhance specific characteristics or meet specific industry standards.
Overall, selecting the right material for custom injection molding is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the final product. Manufacturers work closely with clients to understand their unique needs and recommend suitable material options that meet both functional requirements and cost considerations.
