Choosing the Best Resin for Your Plastic Injection Molded Parts
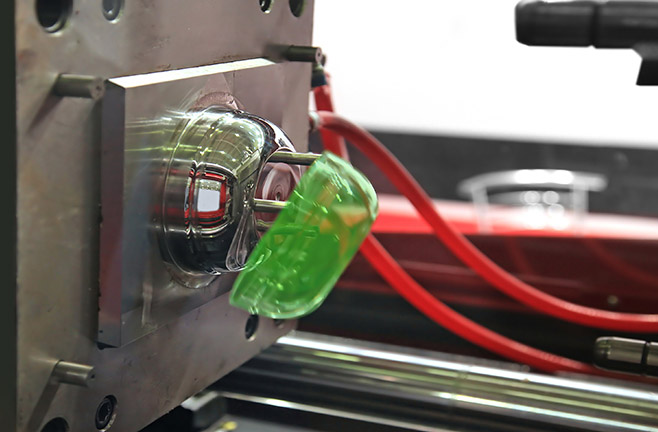
Injection molding has become quite popular amongst manufacturers and businesses across the globe. It is an effective, versatile, and durable process that helps manufacturers produce useful components. Injection molding companies invest heavily in technologies and materials to provide high-quality plastic products to industries like automobiles, defense, and healthcare.
Resins are components that are molded to form plastic parts. They consist of either plastic or polymers. High-quality resins are fundamental to the success of your injection molding project. Various resins can be sourced from suppliers; each has unique characteristics and qualities that make them suitable for various products.
Therefore, you’d need to be careful when choosing the right resin for manufacturing. This comprehensive guide will make the selection process easier for you. Let’s examine how you can choose the ideal resin for your plastic injection molded parts.
Actual Purpose
You need clarity over the intended purpose of your final product or part to select the right resin. Answering the questions below will help you in choosing the resin that is suitable for your product.
- The ideal strength requirement of the molded component?
- Do you require flexibility or rigidness?
- Would the part be exposed to high pressure or extraordinary weight?
- Would the part get exposed to dangerous chemicals?
- Would the part get exposure to extreme heat or cold?
Visual Considerations
When choosing a resin, you’d also need to consider whether the final product has any aesthetic considerations. You’d need to ask yourself the following questions when manufacturing a product that needs to look and feel a certain way.
- Does the product require any color or transparency?
- Does the product require a specific pattern, finish, or texture?
- Does the product need to match a specific color of a larger product assembly?
- Does the product require any embossing?
Regulatory Requirements
Another critical consideration in your resin selection process involves the regulatory requirements in place for your product. So, if you’re exporting parts for the medical, food processing, automobile, or defense industry, the resin and the final product must meet relevant statutory requirements. The following questions will further help you refine your search.
- Does your part fall under the regulatory requirements of different organizations such as the FDA?
- Is your part children-safe?

Identifying The Types of Plastics
Your resin selection process should also include identifying plastics used in product manufacturing. Plastic materials are broadly categorized into two sets – thermosets and thermoplastics.
Thermosets are materials that don’t return to their original shape once melted or heated in a defined shape. These materials set permanently after the molding process, offer high structural integrity, and are ideal for applications that require rigid or permanent parts.
On the other hand, thermoplastics can undergo multiple molding processes without significantly impacting their chemical compounds. Thermoplastics are ideal for manufacturing prototype assembly parts due to their lower melting point.
They offer excellent strength, are lightweight, and are cost-effective in production. They are ideal for mass production or where insert molding or over-molding is required. The only major downside to thermoplastics is that they are prone to warping because of their low melting point.
As mentioned, thermosets can’t be re-shaped, which is why most manufacturers prefer to use thermoplastics in their processes.
Further Refining Selection
If you plan to use thermoplastics in your manufacturing, you should know their categories and types. Thermoplastics can be classified into three categories
- Engineering resins
- Commodity resins
- High-performance resins.
Commodity resins are generally used for everyday plastic applications because they are affordable and process-friendly. Injection molding manufacturers who mass-produce products typically use commodity resins in their processes.
On the other hand, engineering resins offer greater strength but are a bit costly compared to their commodity counterparts. Resins are further classified into two morphologies: Semi-crystalline and amorphous.
Amorphous has some unique characteristics:
- They’ll shrink less compared to semi-crystalline
- They offer greater transparency
- They are quite brittle
Semi-crystalline also has some unique characteristics:
- These resins are opaque
- They offer excellent resistance to abrasion and chemicals
- They do shrink more compared to amorphous resins.

Amorphous and Semi-crystalline Examples
Polystyrene, or PS, is a good example of a commodity resin belonging to the amorphous family. They are extensively used in low-cost applications. A good example of an engineering resin is polycarbonate. It offers great resistance to heat and flames and is used in manufacturing electronic components.
Polyetherimide (PEI) is a common example of a high-performance amorphous resin that offers unprecedented strength and high resistance to heat. The material is extensively used in the aerospace industry.
Polypropylene is an affordable and cost-effective semi-crystalline that is chemical resistant and has flexible properties. This component is widely used to manufacture low-cost products like bottles.
Polyamide (Nylon) is a widely used engineering semi-crystalline resin with excellent abrasion and chemical resistance properties. Due to advancements in materials and technology, bio-based nylon versions are available, making them a sustainable alternative to other similar resins.
Polyetheretherketone is a popular semi-crystalline high-performance resin used to manufacture bearings and pumps because they offer impeccable strength and are heat and chemical-resistant.
Working With PTMS
If you want to work with a premium injection molding service provider that uses high-quality resins for production, you can’t go wrong with PTMS. We have established our reputation as one of the leading injection molding companies in Shenzhen, China.
Since 2002, we have been offering various services, which include mold design, plastic injection tooling, plastic injection molding, silicone parts, metal parts, and product assembly. Most of our products are exported to America, Australia, Japan, and Europe.
You can visit our website to learn more about the comprehensive services we provide to our growing clientele or contact us. We believe in going above and beyond for our customers and meeting their unique needs and requirements.
